- Home
- Project summary
Project summary
Background
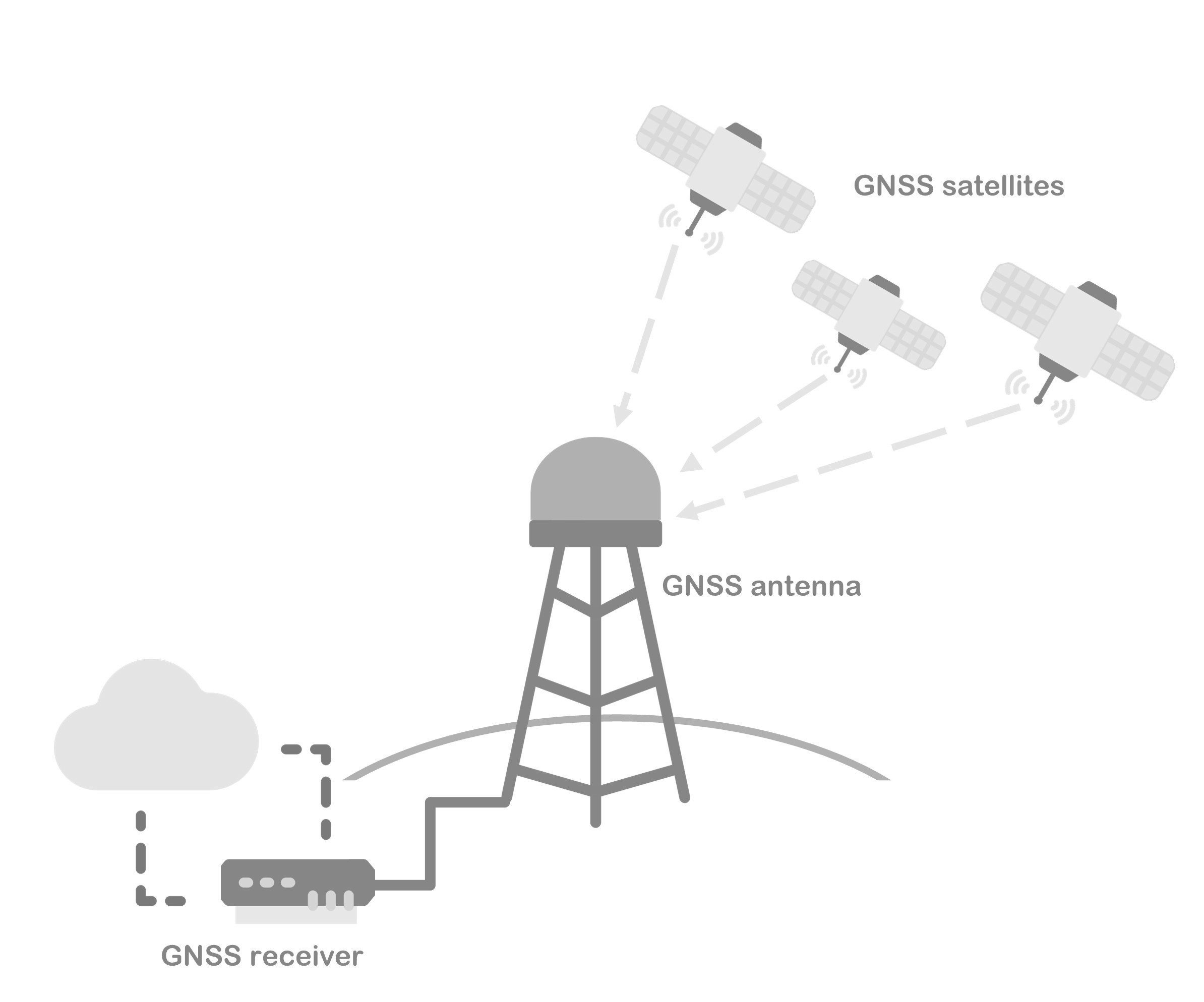 The Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB) maintains repositories containing decades of observation data from Belgian and European stations (EUREF public repository)
permanently tracking Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS, e.g., GPS or Galileo).
These data allow to precisely measure ground deformations, monitor space weather,
study the influence of the atmospheric water vapor trend on climate, provide input for numerical weather predictions, etc.
At the beginning of the FAIR-GNSS project, although many users from different communities were already using ROB's public EUREF repository, the procedures to find and access the data were rather complex and non-machine-readable.
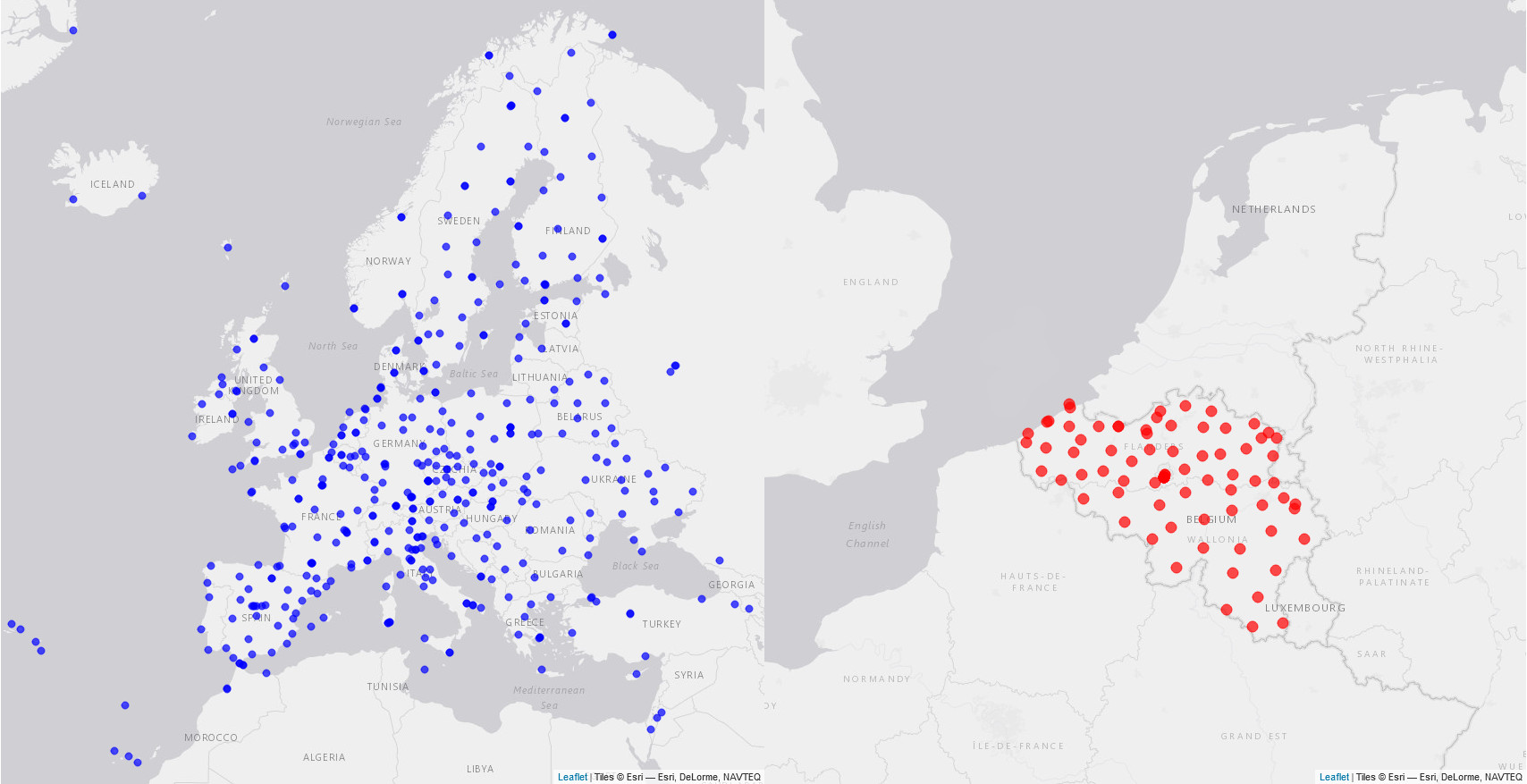
In addition, despite the fact that these GNSS data originate from a significant number of data providers (~100) and can be handled in different ways, provenance information was lacking.
Data licenses were only seldom available and no data citation procedure was in place to recognize the merit of researchers providing the GNSS data.
The Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB) maintains repositories containing decades of observation data from Belgian and European stations (EUREF public repository)
permanently tracking Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS, e.g., GPS or Galileo).
These data allow to precisely measure ground deformations, monitor space weather,
study the influence of the atmospheric water vapor trend on climate, provide input for numerical weather predictions, etc.
At the beginning of the FAIR-GNSS project, although many users from different communities were already using ROB's public EUREF repository, the procedures to find and access the data were rather complex and non-machine-readable.
In addition, despite the fact that these GNSS data originate from a significant number of data providers (~100) and can be handled in different ways, provenance information was lacking.
Data licenses were only seldom available and no data citation procedure was in place to recognize the merit of researchers providing the GNSS data.
Goals
The FAIR-GNSS project attempted to address these needs and aimed to
- facilitate access and re-use of, and increase trust in, ROB’s GNSS data repositories;
- support the preservation of the GNSS data;
- contribute to the standardization of GNSS data citation;
- create a new, modern open data portal for European and Belgian GNSS data
Hence, FAIR-GNSS focused on upgrading ROB’s GNSS data management procedures to align with current best practices in FAIR and Open Data. To achieve its goals, FAIR-GNSS tried to implement FAIR data principles to make data more Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Re-usable (FAIR). These principles serve as guidelines for making scientific data suitable for reuse, by both people and machines, under clearly defined conditions.
Impact
Researchers benefit from the citation metrics associated to GNSS data, as it easily shows the impact of their research data while providing evidence of their usage. FAIR-GNSS’ enhanced data access procedures will enable scientists to easily identify and access those GNSS station data relevant for their specific needs and applications. Indeed, due to the ever-increasing number of GNSS stations, data access has nowadays become too complex and time consuming. In addition, by providing interoperable GNSS data that are easy to integrate with other datasets (e.g., InSAR or seismic data), FAIR-GNSS will facilitate their discoverability within the European Plate Observing System (EPOS). In its practical applications, providing data provenance and adopting user licenses also increase trust in the GNSS data and encourage Small and Medium Enterprises, industries, and start-ups to use these GNSS data and innovate. In short, by making GNSS data more readily available, accessible and citable, FAIR-GNSS paved the way for ROB’s data re-use for multiple applications. FAIR-GNSS presented its results and shared ROB's GNSS team experience on how to implement FAIR data principles via the ""Putting the FAIR principles into practice: the journey of a GNSS data repository" webinar Moreover, FAIR-GNSS showcase FAIR-enabling data repositories to the international scientific GNSS community and engage it in adopting FAIR principles.

